DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS SOLUTION FOR INJECTION/INFUSION 4 MG/ML
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Replacement therapy – adrenocortical insufficiency
Dexamethasone has predominantly glucocorticoid activity and therefore is not a complete replacement therapy in cases of adrenocortical insufficiency. Dexamethasone should be supplemented with salt and/or a mineralocorticoid, such as deoxycorticosterone. When so supplemented, dexamethasone is indicated in:
- Acute adrenocortical insufficiency - Addison’s disease, bilateral adrenalectomy;
- Relative adrenocortical insufficiency - Prolonged administration of adrenocortical steroids can produce dormancy of the adrenal cortex. The reduced secretory capacity gives rise to a state of relative adrenocortical insufficiency which persists for a varying length of time after therapy is discontinued. Should a patient be subjected to sudden stress during this period of reduced secretion (for up to two years after therapy has ceased) the steroid output may not be adequate. Steroid therapy should therefore be reinstituted to help cope with stress such as that associated with surgery, trauma, burns, or severe infections where specific antibiotic therapy is available;
- Primary and secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
Disease therapy
Dexamethasone is indicated for therapy of the following diseases:
Collagen diseases: Systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa, dermatomyositis, giant cell arteritis, adjunctive therapy for short-term administration during an acute episode or exacerbation, acute rheumatic carditis – during an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy.
Pulmonary disorders: Status asthmaticus, chronic asthma, sarcoidosis, respiratory insufficiency.
Blood disorders: Leukaemia, idiopathic thrombocytopaenic purpura in adults, acquired (autoimmune) haemolytic anaemia.
Rheumatic diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, adjunctive therapy for short-term administration during an acute episode or exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
Skin diseases: Psoriasis, erythema multiforme, pemphigus, neutrophilic dermatitis, localised neurodermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, sarcoidosis of skin, severe seborrhoeic dermatitis, contact dermatitis.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis.
Oedema: Cerebral oedema associated with primary or metastatic brain tumours, neurosurgery or stroke, oedema associated with acute non-infectious laryngospasm (or laryngitis).
Eye disorders: Allergic conjunctivitis, keratitis, allergic corneal marginal ulcers, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis, anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy.
Neoplastic states: Cerebral neoplasms, hypercalcaemia associated with cancer, leukaemias and lymphomas in adults, acute leukaemia in children.
Endocrine disorders: Adrenal insufficiency.
Preoperative and postoperative support
Dexamethasone may be used in any surgical procedure when the adrenocortical reserve is doubtful. This includes the treatment of shock due to excessive blood loss during surgery.
Shock
Dexamethasone may be used as an adjunct in the treatment of shock. Dexamethasone should not be used as a substitute for normal shock therapy.
4.3 Contraindications
Administration of dexamethasone is contraindicated in the following cases:
- systemic fungal infections, or other systemic infections unless specific anti-infective therapy is given (see section 4.4 – please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information);
- hypersensitivity to dexamethasone or other corticosteroids or to any component of the injection;
- administration of live virus vaccines (see section 4.4 – please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information);
- In patients with myasthenia gravis, peptic ulcer, osteoporosis or psychoses.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Dosage
Dosage of dexamethasone sodium phosphate is usually expressed in terms of dexamethasone phosphate.
Dosage requirements are variable and must be individualised on the basis of the disease being treated and patient response.
Intravenous (IV) and intramuscular administration
Intravenous or intramuscular dosage usually ranges from 0.5 to 24 mg of dexamethasone phosphate daily. The duration of therapy is dependent on the clinical response of the patient and as soon as improvement is indicated, the dosage should be adjusted to the minimum required to maintain the desired clinical response. Withdrawal of the drug on completion of therapy should be gradual.
Parenteral dexamethasone is generally reserved for patients who are unable to take the drug orally, or for use in an emergency situation.
Shock (of haemorrhagic, traumatic or surgical origin)
The usual dose for the treatment of shock is 2 to 6 mg/kg bodyweight as a single intravenous injection. This may be repeated in 2 to 6 hours if shock persists.
An alternative regimen of 20 mg by intravenous injection initially, followed by continuous intravenous infusion of 3 mg/kg bodyweight per 24 hours, has been suggested. If required for intravenous infusion, dexamethasone phosphate may be diluted with glucose or sodium chloride injection.
High dose therapy should be continued only until the patient’s condition has stabilised and usually for no longer than 48 to 72 hours.
To avoid microbial contamination hazards, infusion should be commenced as soon as practicable after preparation of the mixture and if storage is necessary, store solution at 2 to 8°C. Infusion should be completed within 24 hours of preparation of the solution and any residue discarded.
WARNING: Further diluted solutions which are not clear, or which show evidence of particulate matter contamination, should be discarded.
Cerebral oedema
The treatment schedule and route of administration should reflect the severity and aetiology of the cerebral oedema. Treatment needs to be tailored to the individual response. An initial dose of 10 mg intravenously followed by 4 mg intramuscularly every 6 hours until the symptoms of oedema subside (usually after 12 to 24 hours). After 2 to 4 days the dosage should be reduced and gradually stopped over a period of 5 to 7 days. Patients with cerebral malignancy may require maintenance therapy with doses of 2 mg intramuscularly or intravenously 2 to 3 times daily.
High doses of dexamethasone may be used to initiate short-term intensive therapy for acute cerebral oedema. Following an initial high loading dose, the dose is scaled down over the 7- to 10-day period of intensive therapy, and subsequently reduced to zero over the next 7 to 10 days.
High dose schedule
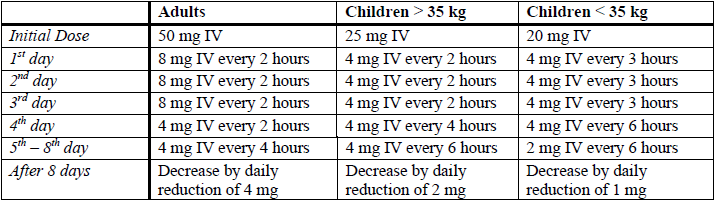
NOTE: The intravenous and intramuscular routes of administration of dexamethasone should only be used where acute illness or life-threatening situations exist. Oral therapy should be substituted as soon as possible.
Intra-synovial & soft tissue injections
Dosage varies with the degree of inflammation and the size and location of the affected area. Injections may be repeated from once every 3 to 5 days (e.g. for bursae) to once every 2 to 3 weeks (for joints). Frequent intra-articular injection may result in damage to joint tissues.
Site of InjectionDosageLarge Joints2 mg to 4 mgSmall Joints800 micrograms to 1 mgBursae2 mg to 3 mgTendon Sheaths400 micrograms to 1 mgSoft Tissue Infiltration2 mg to 6 mgGanglia1 mg to 2 mg
Method of administration
Dexamethasone may be administered intravenously or intramuscularly for systemic effect, or as an intra-synovial or soft tissue injection for local effect.
Contains no antimicrobial agent. For single patient use. Use once only and discard any residue.