META-IODOBENZYLGUANIDINE (I-131) INJECTION FOR THERAPEUTIC USE
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Radiation therapy of tumour-tissue that is capable of retaining iobenguane. These are tumours arising from cells originating embryologically from the neural crest; pheochromocytomas, neuro-blastomas, carcinoids and medullary carcinomas of the thyroid gland (MCT).
4.3 Contraindications
Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Must not be given to premature babies or neonates.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
Therapeutic dose with an amount of [131l]iobenguane individually tailored on the basis of a dosimetric study. The size of the dose as well as the interval(s) between possible multiple administrations are mainly determined by haematological radio-toxicity and the kind of tumour. The more rapid the rate of progression of the tumour, the shorter the interval. Repeat doses may be administered at 6–8 month intervals. The number of doses may vary between 1 and 5. The "fixed" therapeutic dose is (3.7–7.4 GBq).
Elderly population
No special dosage-scheme is required for the elderly patient.
Renal/Hepatic impairment
Careful consideration of the activity to be administered is required since an increased radiation exposure is possible in these patients (see section 5.2 – please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information).
Paediatric population
The recommended dosages are identical for children and adults. Meta-iodobenzylguanidine (rnl) for Therapeutic Use is contraindicated in premature babies and neonates.
Method of administration
The therapeutic dose is administered intravenously, generally as an infusion over a period of 1– 4 hours. lt is recommended that the dose be diluted with 50 ml sterile physiological saline for infusion on thawing and immediately prior to administration by intravenous infusion.
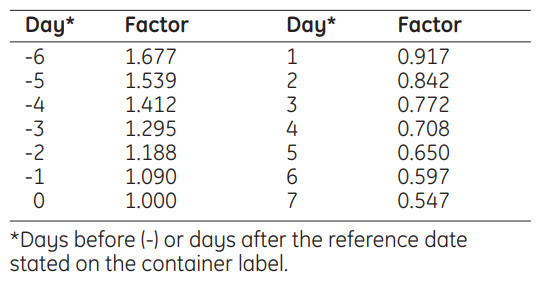
Radioactivity
The volume of iobenguane [131I] for therapeutic use to be injected is calculated by reference to the radioactive concentration at 1200 hours GMT on the day of administration. This is obtained by multiplying the radioactive concentration on the activity reference date by the decay factor given in the following table: